WEEK 7-8: INTERNET AND WORLD WIDE WEB
Computer
networks may be classified according to the scale:-
1. Local area network (LAN)
2.
Metropolitan area network (MAN)
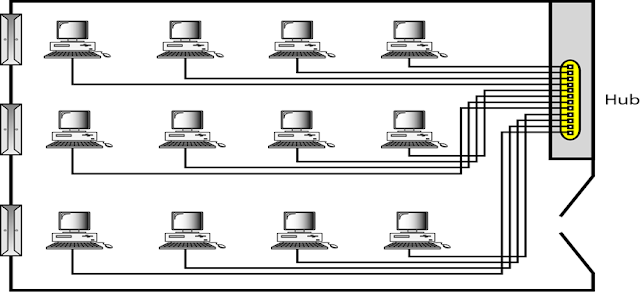
Local area network (LAN)
LAN connects networking devices with in short span
of area, i.e. small offices, home, nternet cafes etc.
Spanned inside a building and operated under single administrative
system
It uses TCP/IP network protocol for
communication between computers
LAN provides a useful way of sharing the resources between end users.
The resources such as printers, file servers, scanners, and internet are easily
sharable among computers
LAN can be wired,wireless, or in both
forms at once.
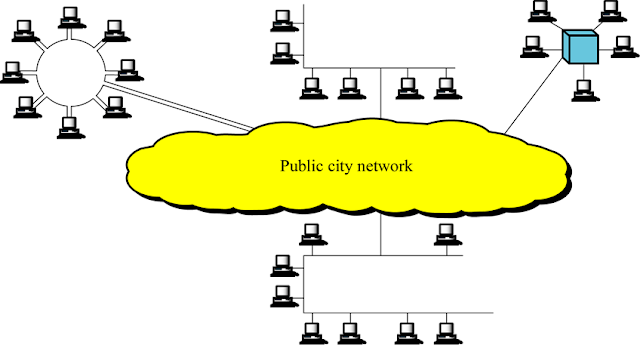
Metropolitan area network (MAN)
MAN generally expands throughout a city
such as cable TV network
Metro Ethernet is a service which is
provided by ISPs
This service enables its users to
expand their Local Area Networks.
For example, MAN can help an
organization to connect all of its offices in a city.
MAN works in between Local Area Network
and Wide Area Network
MAN provides uplink for LANs to WANs or internet
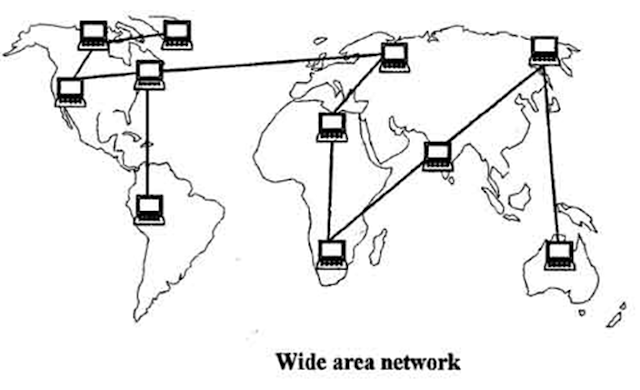
Wide area network (WAN)
WAN connection between computers over
large geographical areas that may comprise a country, a continent, or even the
whole world
Dedicated transoceanic cabling or
satellite uplinks may be used to connect this type of global network
These networks provide connectivity to
MANs and LANs
The Internet itself is the biggest example of WAN
What is Internet
It is a Global network of computers,
(servers or clients) to exchange information.
It is a "network of networks"
that includes millions of private and public, academic, business, and
government networks (local or Global), linked by copper wires, wireless
connections, and other technologies
Intranet
Internal company network that uses
Internet standards (HTML, HTTP & TCP/IP protocols) & software.
Accessed only by authorized persons,
especially members or employees of the organization
Extra-net
Extranet is an Intranet for outside
authorized users using same internet technology.
Website
Is a collection of an electronic pages that stores the information of a certain organization.
Type of website
Static : This is type of website that
all user can see and interact with the same content in it.example www.suza.ac.tz
Dynamic:This is type of website that
any user interact with different content in it.example Zalongwa.
WEB BROWSER
A web browser (commonly referred to as a browser) is a software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI/URL) that may be a web page, image, video or other piece of content. Hyperlinks present in resources enable users easily to navigate their browsers to related resources.
Although browsers are primarily intended to use the World Wide Web, they can also be used to access information provided by web servers in private networks or files in file systems.
The major web browsers are Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer/Microsoft Edge, Opera, and Safari.
A web browser (commonly referred to as a browser) is a software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI/URL) that may be a web page, image, video or other piece of content. Hyperlinks present in resources enable users easily to navigate their browsers to related resources.
Although browsers are primarily intended to use the World Wide Web, they can also be used to access information provided by web servers in private networks or files in file systems.
The major web browsers are Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer/Microsoft Edge, Opera, and Safari.
Mozilla Firefox vs Internet
Explorer
Everyone who’s been on the
Internet knows what Internet Explorer is. Internet browsers are an essential
part in fully utilizing the Internet to the fullest. But, there are also other
options and one of them is Mozilla’s Firefox. There is a big difference though
when it comes to popularity as Internet Explorer is still the most used browser
in the world with Firefox as a distant second.
The main reason behind the popularity of Internet Explorer is its availability. It comes bundled with every version of Windows and users can simply update to new versions when they become available. Because Windows is the biggest operating system for personal computers, Internet Explorer already has such a huge advantage. Firefox comes preinstalled with certain Linux distributions but these are used on quite a small percentage of computers. If you want Firefox on Windows, you need to download an installer; commonly through Internet Explorer.
1. Internet Explorer is the most popular browser while Firefox is only second
2. Internet Explorer is bundled with Windows while Firefox is not
3. Internet Explorer is available only on Windows while Firefox is available for other operating systems
4. Internet Explorer is slow than Firefox
5. Internet Explorer is less secure than Firefox
The main reason behind the popularity of Internet Explorer is its availability. It comes bundled with every version of Windows and users can simply update to new versions when they become available. Because Windows is the biggest operating system for personal computers, Internet Explorer already has such a huge advantage. Firefox comes preinstalled with certain Linux distributions but these are used on quite a small percentage of computers. If you want Firefox on Windows, you need to download an installer; commonly through Internet Explorer.
1. Internet Explorer is the most popular browser while Firefox is only second
2. Internet Explorer is bundled with Windows while Firefox is not
3. Internet Explorer is available only on Windows while Firefox is available for other operating systems
4. Internet Explorer is slow than Firefox
5. Internet Explorer is less secure than Firefox
Home Page
When you launch a Web browser, it
automatically opens a new window with a default home page--usually Google.com
or Bing.com--loaded and ready to go. You can set the home page to any website
you prefer, however. Here's how to change the home page in Microsoft Internet
Explorer, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox
Change Your Internet Explorer
Home Page
1. Click Tools, Internet
options. Windows Vista/7 users may need to press the Alt key
for the menu to appear
2. The
Internet Options window will open. Click the General tab, and
type in the address of the website you want as your start page under the 'Home
page' heading.
3. Click Apply, OK to
close the window.
Change Your Google Chrome Home
Page
1. Click
the wrench icon in the top-right corner of the browser.
2. Select Options
3. In
the 'On startup' section, select Open the home page.
4. In
the 'Home page' section, choose Open this page and type in the
address of the website you would like as your start page.
5. The
settings apply immediately. You may close the settings tab now.
Change Your Mozilla Firefox Home
Page
1. Click
the Firefox menu at the top-left portion of the browser.
2. Click
the Options menu, and then Options.
3. The
Options window will open. Go to the Startup section and select When
Firefox starts: Show my home page.
4. In
the Home Page field, type in the website address you want to
use as your home page.
5. Click OK.
URL - Uniform Resource Locator
URL is the abbreviation of Uniform Resource Locator.
It is the global address of documents and other resources on the World Wide
Web. For example, www.webopedia.com is a URL. A URL is one type of Uniform Resource Identifier
(URI); the generic term for all types of names and addresses that
refer to objects on the World Wide Web.
PARTS OF
A URL
The first part of the URL is
called a protocol identifier and it indicates what protocol to
use, and the second part is called a resource name and it
specifies the IP address or the domain name where the resource is located. The
protocol identifier and the resource name are separated by a colon and two
forward slashes.
For example, the two URLs below
point to two different files at the domain webopedia.com. The
first specifies an executable file that should be fetched using the FTP
protocol; the second specifies a Web page that should be fetched using the HTTP
protocol:
ftp://www.webopedia.com/stuff.exe
http://www.webopedia.com/index.html
http://www.webopedia.com/index.html
INTERNET
SERVICES
History of the world wide
web
The World Wide Web
("www" or simply the "web") is a global information
medium which users can read and write via computers connected to the internet.
The term is often mistakenly used as a synonym for the internet itself, but the
web is a service that operates over the internet, just as e-mail also does. The
history of the internet dates back significantly further than that of the world
wide web.
Email
Electronic mail, or email,
is a method of exchanging digital messages between people using digital devices
such as computers, tablets and mobile phones. Email first entered substantial
use in the 1960s and by the mid-1970s had taken the form now recognised as
email. Email operates across computer networks, which in the 2010s is primarily
the Internet. Some early email systems required the author and the recipient to
both be online at the same time, in common with instant messaging. Today's
email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept,
forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are
required to be online simultaneously; they need to connect only briefly,
typically to a mail server or a webmail interface, for as long as it takes to
send or receive messages.
Originally an ASCII text-only
communications medium, Internet email was extended by Multipurpose Internet
Mail Extensions (MIME) to carry text in other character sets and multimedia
content attachments. International email, with internationalized email
addresses using UTF-8, has been standardized, but as of 2016 it has not been
widely adopted.
The history of modern Internet
email services reaches back to the early ARPANET, with standards for encoding
email messages published as early as 1973 (RFC 561). An email message sent in
the early 1970s looks very similar to a basic email sent today. Email played an
important part in creating the Internet,and the conversion from ARPANET to the
Internet in the early 1980s produced the core of the current services.
Social network
A social network is
a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or
organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between
actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing
the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories
explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these
structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns,
locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics.
Social networks and the analysis
of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from
social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel
authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of
triads and "web of group affiliations". Jacob Moreno is credited with
developing the first sociograms in the 1930s to study interpersonal
relationships. These approaches were mathematically formalized in the 1950s and
theories and methods of social networks became pervasive in the social and
behavioral sciences by the 1980s. Social network analysis is now one of the
major paradigms in contemporary sociology, and is also employed in a number of
other social and formal sciences. Together with other complex networks, it
forms part of the nascent field of network science.
Surfing the Internet
Surfing the Internet' is not to
be confused with the phrase 'browsing the Internet' which refers to exploring
the web with a clear-cut objective but without any planned search strategies.
Searching the web refers to exploring the Internet with a definite in both
strategy and objective.
Surfing the Internet has been
likened to the ironic term 'channel surfing', which is used to describe
randomly changing TV channels. Its only relation to actual surfboarding has to
do with the notion of 'going with flow' when surfing.
Web search engine
A web search engine is a software
system that is designed to search for information on the World Wide Web. The
search results are generally presented in a line of results often referred to
as search engine results pages (SERPs). The information may be a mix of web
pages, images, and other types of files. Some search engines also mine data
available in databases or open directories. Unlike web directories, which are
maintained only by human editors, search engines also maintain real-time
information by running an algorithm on a web crawler.


No comments:
Post a Comment